Introduction
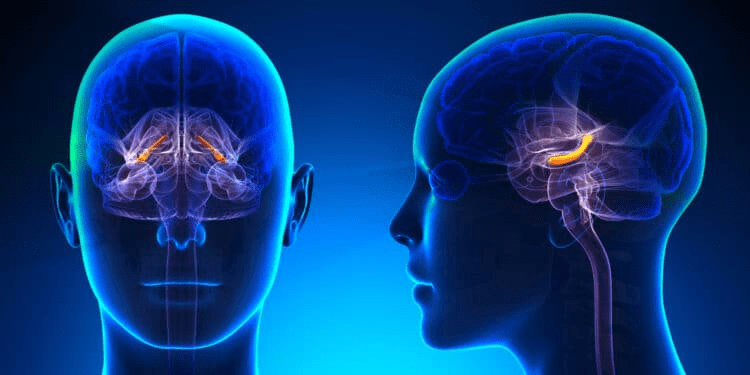
Hippocampal volumetry is a critical technique in neuroscience and medical research that measures the size of the hippocampus, a brain structure essential for memory and cognition. Changes in hippocampal volume are linked to various neurological and psychiatric disorders, making this measurement invaluable in both research and clinical settings. This article explores the methods, applications, and clinical significance of hippocampal volumetry.
1. What is Hippocampal Volumetry?
Hippocampal volumetry refers to the quantitative assessment of hippocampal size, typically using imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The hippocampus plays a crucial role in learning, memory formation, and spatial navigation. Measuring hippocampal volume is essential for understanding its involvement in aging, cognitive decline, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.
2. Methods and Techniques for Hippocampal Volumetry
MRI-Based Volumetric Analysis
MRI is the gold standard for measuring hippocampal volume due to its high-resolution imaging capabilities. The process involves segmenting the hippocampus from MRI scans and calculating its volume using specialized software.
Popular Software Tools
- FreeSurfer: A widely used automated tool for brain segmentation and volumetric analysis.
- FSL (FMRIB Software Library): Provides tools for brain image analysis, including hippocampal segmentation.
- ANTs (Advanced Normalization Tools): Used for brain registration and segmentation in volumetric studies.
Step-by-Step Process of Hippocampal Volumetry
- Image Acquisition: High-resolution MRI scans are obtained.
- Preprocessing: Images are corrected for artifacts and aligned.
- Segmentation: The hippocampus is identified and segmented using software tools.
- Volume Calculation: The software calculates the hippocampal volume based on voxel measurements.
- Data Interpretation: Results are analyzed in relation to normative data or clinical findings.
Challenges in Obtaining Accurate Measurements
- Variability in segmentation methods.
- Differences in MRI scan quality and resolution.
- Inter-subject anatomical differences affecting volume calculations.
3. Applications in Research and Medicine
Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Reduced hippocampal volume is an early marker of Alzheimer’s, aiding in early diagnosis and monitoring disease progression.
- Epilepsy: Hippocampal sclerosis, characterized by volume loss, is a hallmark of temporal lobe epilepsy.
Mental Health Conditions
- Depression and PTSD: Studies have linked reduced hippocampal volume to mood disorders, indicating its role in emotional regulation.
- Schizophrenia: Patients often show hippocampal atrophy, contributing to cognitive deficits.
Cognitive Neuroscience and Brain Mapping
Hippocampal volumetry is essential for studying brain development, memory processes, and the impact of aging on cognition.
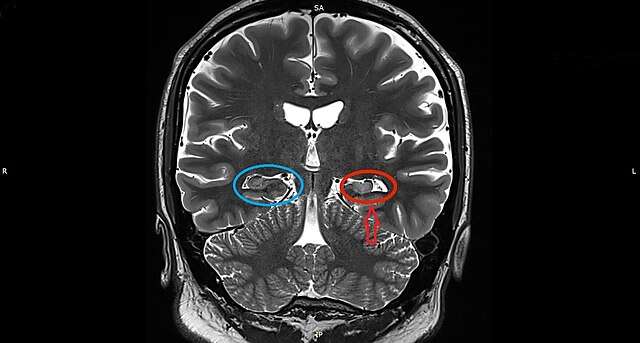
4. Clinical Significance of Hippocampal Volumetry
Early Diagnosis of Diseases
Hippocampal atrophy serves as a biomarker for neurodegenerative disorders, allowing for early interventions and targeted treatments.
Correlation with Cognitive Decline
Smaller hippocampal volumes are associated with memory impairment and cognitive decline, making volumetry a valuable tool in dementia research.
Case Studies and Clinical Examples
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): Reduced hippocampal volume predicts conversion from MCI to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Stroke Patients: Volumetric analysis helps assess post-stroke cognitive recovery.
5. Recent Advances and Breakthroughs
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI and machine learning algorithms enhance segmentation precision and automate volumetric analysis.
- High-field MRI (7T) provides superior resolution for more detailed hippocampal assessment.
Key Findings from Recent Studies
- Studies suggest that lifestyle factors, such as exercise and diet, influence hippocampal volume.
- New biomarkers, including hippocampal subfield atrophy patterns, improve diagnostic accuracy.
Future Directions
- Integration of multimodal imaging (e.g., PET-MRI) for comprehensive brain analysis.
- Development of standardized volumetric protocols for clinical use.
6. Challenges and Limitations
Variability in Measurements Across Studies
Different imaging protocols and analysis techniques lead to inconsistencies in volumetric data.
Ethical Considerations in Neuroimaging
Ensuring patient privacy and data security in neuroimaging research is crucial.
Limitations in Clinical Applications
Despite its potential, hippocampal volumetry is not yet a standalone diagnostic tool due to variability in interpretation and the need for complementary assessments.
Read Also: Natural Ways to Treat Hippocampal Atrophy
Conclusion
Hippocampal volumetry is a powerful tool in neuroscience and medicine, offering insights into brain function, disease progression, and cognitive health. With ongoing advancements in imaging technology and data analysis, its clinical applications continue to expand. Further research and collaboration among scientists and clinicians will enhance its accuracy and utility, ultimately benefiting patients with neurological and psychiatric conditions.